Precipitation hardening stainless steels are materials that maintain corrosion resistance*1 as stainless steel while its strength can be increased by precipitation hardening (age hardening)*2 .
In particular, SUS631 is a soft metastable austenite phase in the annealed (solution heat-treated) state. As a result, it can withstand complex machining as well as austenitic stainless steel, and its strength can be increased by precipitation hardening (heat treatment) after machining.
TOKKIN supplies three types of steel: SUS631 (17-7PH), SUS632J1 (15-7PH), and TOKKIN™ 350, and can propose steel grades according to customer applications and processing methods.
*1 The general order of corrosion resistance for each type is as follows: austenitic > precipitation hardening > ferritic.
*2 Precipitation hardening refers to the process of artificially performing aging treatment (precipitation hardening) after solution heat treatment. Typical examples of precipitation hardening are stainless steels in the 600 series and maraging steels introduced on this page.
Diaphragms, Bellows, Reed Valves, Band Saws, Mask Frame Springs, Various Springs, Bellows, etc.

Thickness : 0.030mm-3.0mm *Availability may vary by steel grade.
Width : 3.0mm-300mm *Contact Sales if your desired values is over 300mm.
Length : COIL or SHEET less than L2000mm
| SUS631(17-7PH) | The most typical precipitation-hardening grade that can be heat-treated to increase hardness while retaining the excellent performance of 18-8 stainless steel. By applying various heat treatments, ranging from the softest solution-treated to the hardest pressure-rolled, depending on the processing and application, we can obtain materials with a strength second only to high-carbon martensitic quenched materials. In the solution heat-treated state, the elongation rate exceeds 30%, enabling strong processing such as drawing. Please note that the material is weakly magnetic in the solution heat-treated state, but becomes quite strongly magnetic after precipitation hardening treatment. |
|---|---|
| SUS632J1(15-7PH) | The solution heat-treated state (austenite phase) of SUS631 is soft and can be processed in various ways, but requires two or more heat treatments of martensitization and precipitation hardening to increase its strength. Since SUS632J1 is always in martensitic phase with or without solution treatment, it can be strengthened with only one precipitation hardening heat treatment. Solution heat-treated SUS632J1, although a martensitic phase, can be lightly machined due to its low carbon content and toughness. There are two types of finishes: solution heat-treatment finish and rolled finish. The rolled finish has higher strength, but it is not as strong as SUS631. This steel grade exhibits strong magnetism in all states. |
| TOKKIN™ 350 [TOKKIN Original Grade] |
TOKKIN™ 350 is a Cr-Ni-Mo stainless steel. In solution annealed and annealed conditions, it boasts excellent workability and high strength due to heat treatment, and it has excellent proof stress and repeated fatigue strength. Compared to other precipitation hardening stainless steels, the addition of molybdenum provides superior corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance, and the absence of aluminium and titan provides good weldability. |
Unless otherwise specified, we manufacture in accordance with JIS standards. Equivalent overseas standards are for reference only.
Please scroll horizontally to view.
| Grade | Japan | USA | Europe | Internatinal Standards | Others | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JIS | UNS | AISI/ASTM | EN | ISO | ||
| SUS631 (17-7PH) |
G4313, G4305 | S17700 | 631 | 1.4568 | X7CrNiAl17-7 | |
| SUS632J1 (15-7PH) |
G4313 | |||||
| TOKKIN™ 350 | - | S35000 | 633 | - | - | AMS5548 |
Please scroll horizontally to view.
[mass%]
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | Fe | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUS631 (17-7PH) |
0.09 max | 1.00 max | 1.00 max | 0.040 max | 0.030 max | 16.00- 18.00 |
6.50-7.75 | - | Bal. | Al 0.75-1.5 |
| SUS632J1 (15-7PH) |
0.09 max | 1.00-2.00 | 1.00 max | 0.040 max | 0.030 max | 13.50- 15.50 |
6.50-7.75 | - | Bal. | Cu 0.40-1.00 Ti 0.20-0.65 |
| TOKKIN™ 350 | 0.07-0.11 | 0.50 max | 0.50-1.25 | 0.040 max | 0.030 max | 16.00- 17.00 |
4.00-5.00 | 2.50-3.25 | Bal. | N 0.07-0.13 |
Please scroll horizontally to view.
| Grade | Density [g/cm3 ] |
Specific Heat [J/(kg・K)] |
Electrical Resistance [μΩ・cm] |
Young's Modulus [GPa] |
Thermal Expansion [×10-6/K] |
Thermal Conductivity [W/(m・K)] |
Melting Point [℃] |
Magnetic Permeability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUS631 (17-7PH) |
7.81 | 420 | 79 | 200 | 15.3 (0-100℃) |
16.3 | 1414-1447 | Nonmagnetic in the solution heat-treated state, but becomes magnetic after processing and quite strongly magnetic after precipitation hardening treatment. |
| SUS632J1 (15-7PH) |
7.74 | 502 | 100 | 196 | 10.9 (0-100℃) |
15.9 (100℃) |
- | Strong |
| TOKKIN™ 350 | 7.92 | 461 | 79 | 200 | 15.2 (25-100℃) |
15.4 (100℃) |
- | - |
Please scroll horizontally to view.
| As annealed / As cold rolled | After Precipitation Hardening Treatment | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | Condition | Temper Designation |
Hardness [HV] |
Tensile Strength [MPa] |
Elongation [%] |
V-bending 0.5t |
W-bending 1.0t |
Heat Treatment Designation |
Hardness [HV] |
Tensile Strength [MPa] |
Yield Strength [MPa] |
| SUS631 (17-7PH) |
Material A | BA, 2B | 200 max |
1030 max |
20 min |
R90° | R90° | TH1050 | 345 min |
1140 min |
960 min |
| RH950 | 392 min |
1230 min |
1030 min |
||||||||
| Material C | 1/2H | 350 min |
1080 min |
5 min |
1.5t R90° | 2.0t R90° | CH | 380 min |
1230 min |
880 min |
|
| 3/4H | 400 min |
1180 min |
- | - | - | 450 min |
1420 min |
1080 min |
|||
| H | 450 min |
1420 min |
- | - | - | 530 min |
1720 min |
1320 min |
|||
| EH | 480 min |
1620 min |
- | - | - | 560 min |
1900 min |
1570 min |
|||
Please scroll horizontally to view.
| As annealed / As cold rolled | After Precipitation Hardening Treatment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | Temper Designation |
Hardness [HV] |
Yield Strength [MPa] |
Tensile Strength [MPa] |
Hardness [HV] |
Yield Strength [MPa] |
Tensile Strength [MPa] |
| SUS632J1 (15-7PH) |
1/2H | 350 max | - | 1200 max | 400 min | 1250 min | 1300 min |
| 3/4H | 420 max | - | 1450 max | 480 min | 1500 min | 1550 min | |
Please scroll horizontally to view.
| Grade | Thickness | Annealed(BA, 2B) | SCT850 Condition | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness [HV] |
Tensile Strength [MPa] |
Yield Strength [MPa] |
Elongation [%] |
Hardness [HV] |
Tensile Strength [MPa] |
Yield Strength [MPa] |
Elongation [%] |
||
| TOKKIN™ 350 | 0.038 < t ≤ 0.051 | Negotiable* | 1393 max | 641 max | 9 min | Negotiable* | 1276 min | 1034 min | 4 min |
| 0.051 < t ≤ 0.127 | Negotiable* | 1372 max | 627 max | 10 min | Negotiable* | 1276 min | 1034 min | 6 min | |
| 0.127 < t ≤ 0.254 | Negotiable* | 1351 max | 614 max | 12 min | Negotiable* | 1276 min | 1034 min | 6 min | |
| 0.254 < t ≤ 0.508 | Negotiable* | 1331 max | 600 max | 14 min | Negotiable* | 1276 min | 1034 min | 8 min | |
* Hardness is provided for reference only. Please contact us for more information.
Solution treatment (solution treatment) is followed by artificial age hardening (precipitation hardening). Typical examples are the precipitation hardening stainless steels (No. 600 series) and maraging steels shown on this page.
Click here for a list of precipitation hardenable materials we supply.
The precipitation hardening heat treatment methods for each steel grade are as follows.
SUS631 is hardened from the solution treatment (annealed) condition (material A) by one of the following three methods.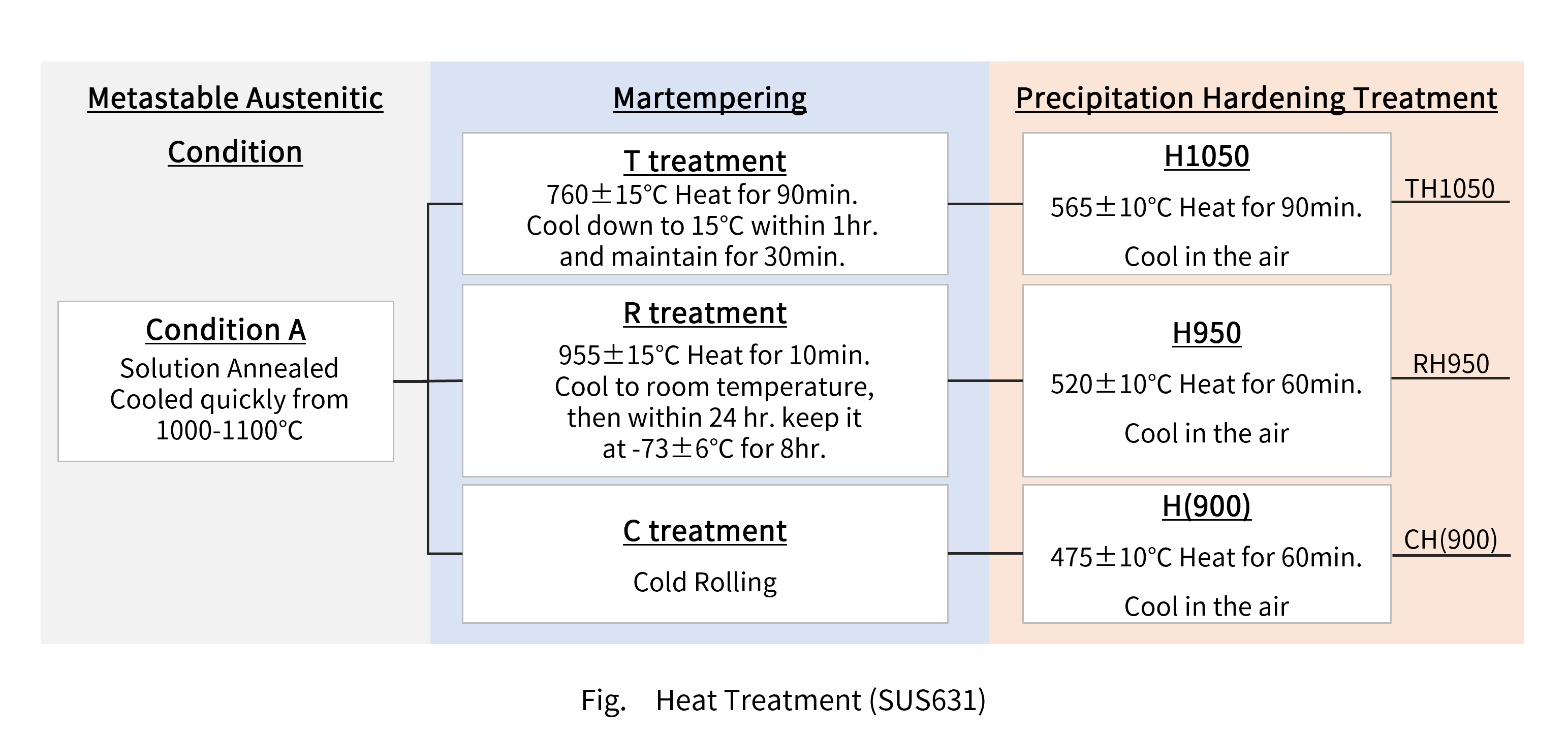
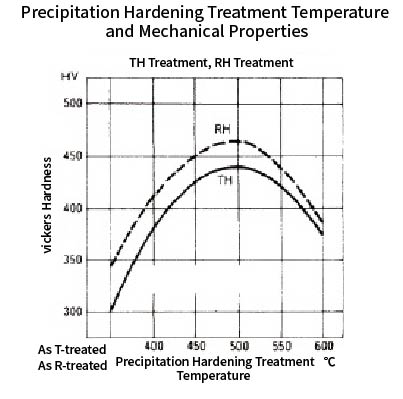
The upper and middle TH1050 and RH950 treatments are hardened by a two-step heat treatment process. The first T and R treatments are primary hardening heat treatments to martensitize the metastable austenite phase A material as in quenching, while the second H treatment completely hardens the material by precipitation hardening, which is the main feature of this steel grade.
*Precipitation hardening is not possible even if only H treatment is performed in the solid solution state (Condition A material).
*TOKKIN does not have the equipment to perform TH and RH hardening treatment, so these heat treatments are performed by the customer.
The CH(900) treatment in the lower row is cold-work hardening instead of martensitizing by heat treatment, and we provide it after cold rolling to an appropriate hardness(Condition C material) .
Therefore, for customer use, only one more precipitation hardening heat treatment (H treatment) is required.
Precipitation hardening heat treatment conditions for SUS632J1 are as follows:
480°C x 1 hour holding
While SUS631 requires intermediate hardening treatment (martensification treatment), SUS632J1 can be hardened by only one heat treatment in any condition.
TOKKIN™ 350 is precipitation hardened from the annealed state to obtain high strength through two treatments: primary hardening, which transforms the metastable austenite structure in the annealed state into martensite, and precipitation hardening, which completely hardens the structure.
The temperature conditions are as shown in the SCT850 heat treatment conditions below.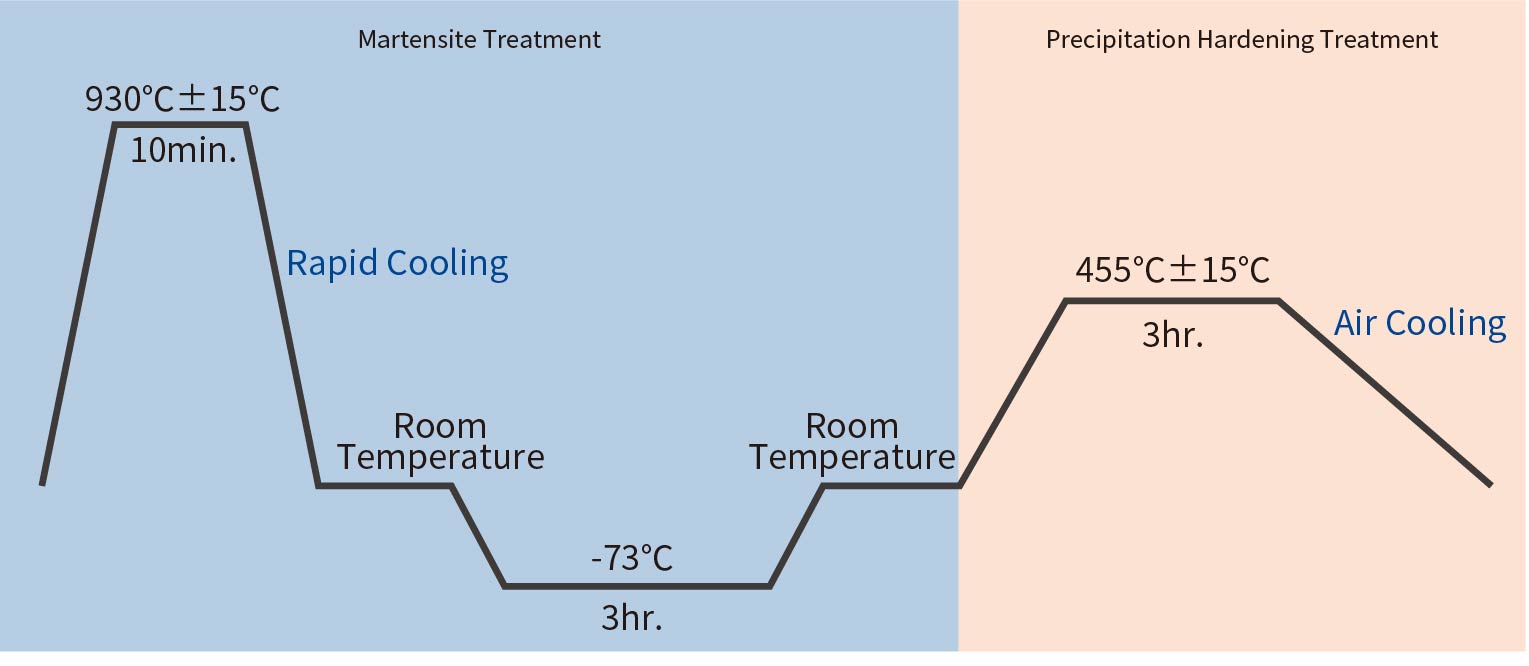
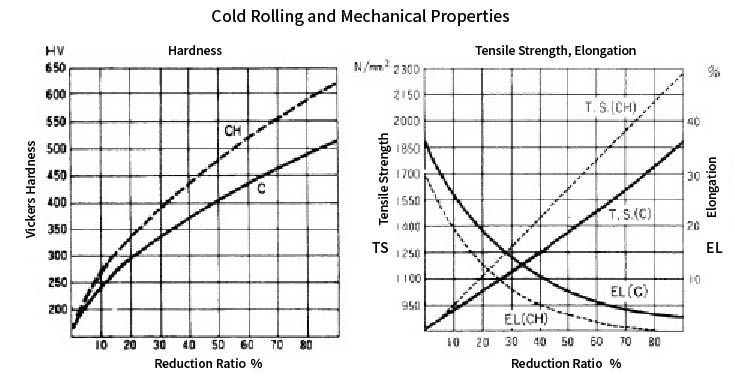
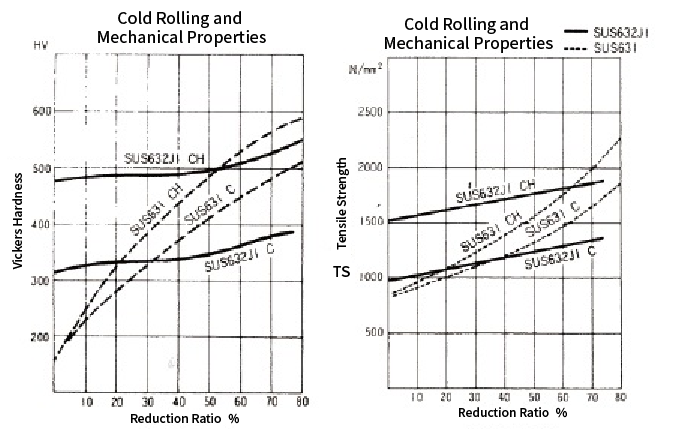
(1)Hardness increase depends on the cold rolling rate.
The following figure (left), "Cold Rolling and Mechanical Properties," shows reduction ratio-hardness and hardness after precipitation hardening.
SUS631 C (dashed line) has a large increase in hardness as the rolling ratio increases, on the opposite, SUS632J1 C (solid line), even if the rolling ratio is increased, the hardness does not increase as much as SUS631 C.
SUS632J1 has a certain degree of strength without strong cold working, and its hardness increase due to cold working is smaller, it is recommended for those who are concerned about directional properties or who require formability and punching workability.
(2)The amount of hardness increase due to precipitation hardening heat treatment (H treatment) differs.
When H treatment (precipitation hardening heat treatment) is applied to C material (cold-rolled material) of SUS631, the maximum increase in hardness (the higher the rolling ratio, the greater the increase in hardness after H treatment) is about HV80-90, but with SUS632J1, the increase is over HV150 regardless of rolling ratio.
Thus, for SUS631, it is possible to greatly increase the hardness by applying TH1050 or RH950 treatment to A material (soft material of HV200 or less), so we recommend A material of SUS631 if complex shapes are required.
However, for A material, martensitization treatment (T treatment, R treatment) must be performed prior to H treatment, so please pay attention to the heat treatment conditions.
Although precipitation hardening stainless steels are generally scarce in circulation, we can provide the following services;
We manufacture TOKKIN 350 and various other metals for bellows, and we can propose materials and specifications according to required properties such as strength, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance.
It is used for springs because it can obtain high strength through cold working and heat treatmentis. please click here to see difference of each steel grade.