Clad Metals are the materials consisting of two or more different metals bonded together.
It is a highly functional metal material with composite properties that cannot be obtained with a single material. In Clad Metals, the boundary surfaces between dissimilar metals are diffusion bonded (alloyed by elemental diffusion), so there is less concern about delamination as in plating. Clad Metals can help reduce total costs by reducing processes and lead time and improving quality.
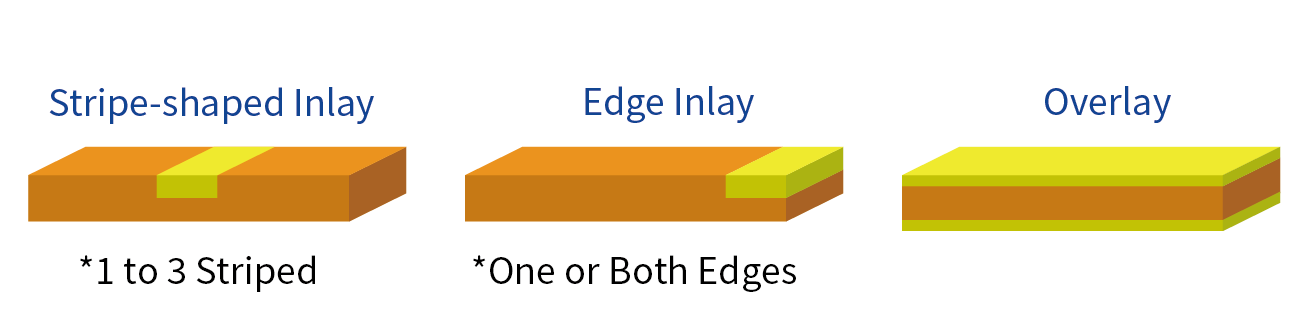
Double-sided inlay (edge inlay) cladding and double-sided edge inlay cladding is also available upon request.
please feel free to contact us.
Resistors, Thermal Protectors, Printer Springs, Connector Shells, Various Contacts, Keyboard Springs, Shielding Cases, Surge Absorbers, Relays, Power Window Contacts, Battery Parts, Membrane Switches, Fire Alarm Contacts, etc.

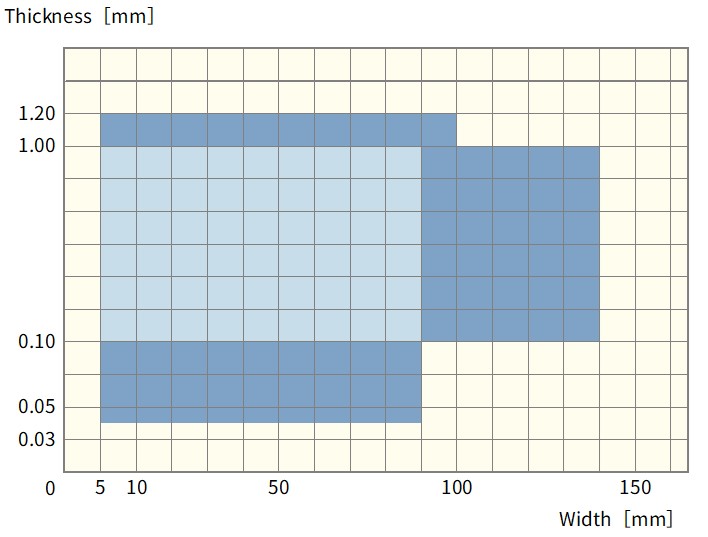
Total Thickness: 0.040~1.2mm
Width : About 5.0 ~ 140mm
*The manufacturable range will vary depending on combinations. Please contact us for details.
Manufacturable range
Please contact our sales representative
The following figure shows the combinations of clad metals we have manufactured so far. Other combinations will be considered upon request,
Please feel free to contact us.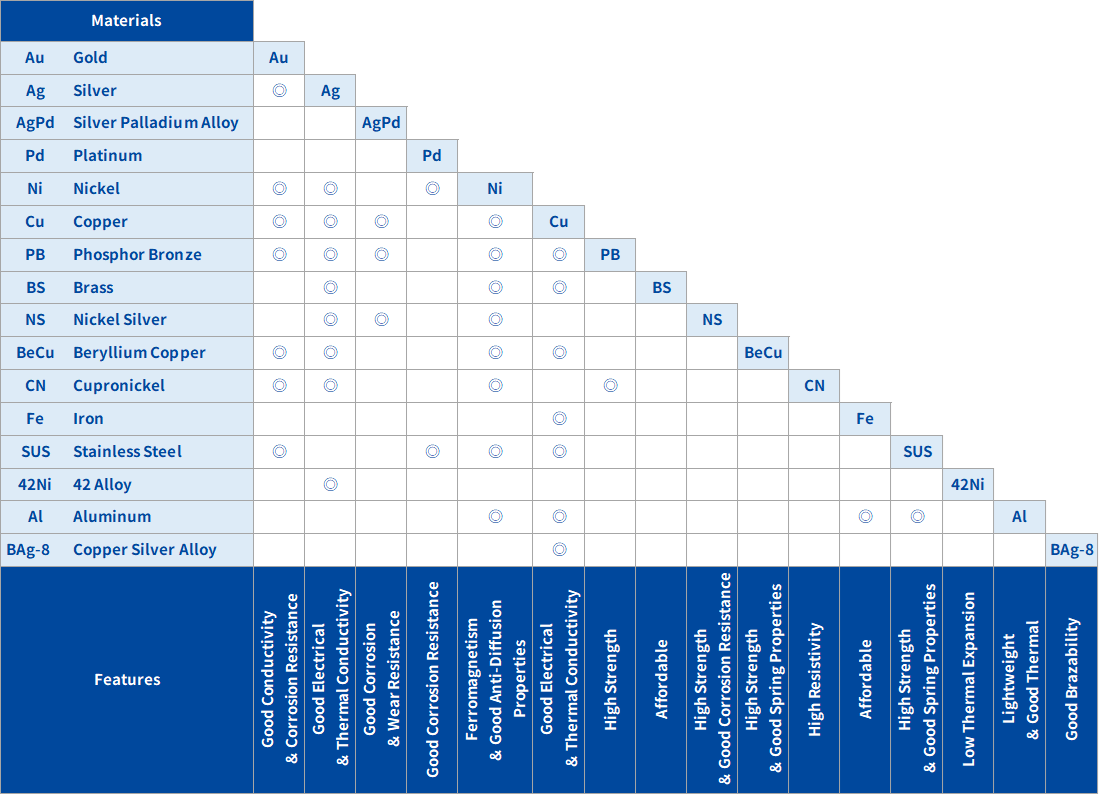
Please scroll horizontally to view.
| Material | Nominal Composition [wt%] |
Hardness [HV] |
Electrical Conductivity [IACS%] |
Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure silver | 99.9Ag | 26 | 106 | For low-current applications |
| Silver-Copper | 90Ag10Cu | 62 | 89 | Large contact pressure, suitable for sliding applications |
| 80Ag20Cu | 85 | 82 | ||
| Silver-Palladium | 70Ag30Pd | 70 | 11 | Excellent oxidation resistance |
| 60Ag40Pd | 102 | 7.7 | ||
| Silver-Palladium Copper |
40Ag40Pd20Cu | 190 | 7.7 | Low-cost six-part alloy suitable for sliding applications |
| Silver-Nickel | 85Ag15Ni | 73 | 88 | Better wear resistance and welding resistance than Ag |
| Silver braze (BAg-8) | 72Ag28Cu | - | - | Liquidus temperature: 780°C |
Please scroll horizontally to view.
| Name | Code | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Copper | C1020 | High Electrical and Thermal Conductivity |
| Phosphor Bronze | C5102 | High strength and Spring Properties |
| C5191 | ||
| C5212 | ||
| Brass | C2600 | Workability and Low Cost |
| C2680 | ||
| Pure Aluminum | A1050/A1100 | Lightweight and High Thermal Conductivity |
| Pure Nickel | Ni | High Corrosion Resistance and Strong Magnetism |
| Pure Iron | SPCC | Versatility, Workability, and Low Cost |
| SUY | Deep Drawability and Electromagnetic Applications | |
| Stainless Steel | SUS304 | High Corrosion Resistance, Workability, and Spring Properties |
| SUS430 | High Corrosion Resistance, Low Cost, and Magnetism |
|
| Iron-Nickel Alloys | 36Ni | Low Thermal Expansion (mainly used for sealing electron tubes) |
| 42Ni | ||
| Iron-Nickel-Cobalt Alloys | KOV | |
| Copper-Nickel | CN49 | Resistance Alloys |
| Copper-Manganese | CM | |
| Nickel-Chromium | NCH-1 |
We manufacture custom clad materials in overlay, inlay, edgelay, and stripe designs according to your desirable width, thickness, distance away from the edge, and numbers of strip.
Clad metals offer the opportunity to combine desirable properties and/or characteristics of individual metals and alloys into a composite materials “system” that brings infinite possibility!
This is a new cladding method that forms a Layer on a base material using the "Cold spray (CS: low-temperature thermal spraying)" technology, in which metal powder is accelerated to supersonic speeds and sprayed in a solid state.
It can be applied to resin and ceramics.